 In this little note, I want to describe a simple logging module for C programs in Linux. I’m using this code for years in my projects. This module supports different types of output “targets” – files, syslog, and stdout.
In this little note, I want to describe a simple logging module for C programs in Linux. I’m using this code for years in my projects. This module supports different types of output “targets” – files, syslog, and stdout.
Every printed message is the preceded name of the program, current date/time, type of the message – debug/error/warning/etc.
This is very useful, can improve readability, and can provide easy filtering of the required messages. The programmer can configure the logging level in a runtime.
The logging module provides a set of functions for configuring and message printing.
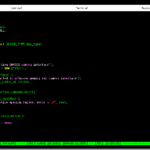
/* * Logging methods by levels */ void log_error(char* format, ...); void log_warning(char* format, ...); void log_status(char* format, ...); void log_debug(char* format, ...); /* * Log level configurator * Default is LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS */ #define LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR 0 #define LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS 1 #define LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS_DEBUG 2 void logger_set_log_level(const int level); /* * Set target type * Default is syslog */ void logger_reset_state(void); int logger_set_log_file(const char* filename); void logger_set_out_stdout();
As you can see, logging methods supported variable types of the arguments, so you can use these methods like a regular printf providing different types of formats and argument types.
Different logging levels can be configured, which can be used for suppressing some message types if needed, without program recompilation. The default log level is ERROR/WARNING/STATUS, and DEBUG messages are disabled in a normal state.
By default, all messages are going to the syslog. But you can specify a separate text file or use regular stdout. In file mode, logger automatically handles non-existing files creating a new file or appending the message to the already existing file.
Here is the full source code of this logging module:
#include <syslog.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "logger.h"
/*
* Program name variable is provided by the libc
*/
extern const char* __progname;
/*
* Logger internal sctructure
*/
struct logger_t {
int max_log_level;
int use_stdout;
FILE* out_file;
void (*logger_func) (const int level, const char*);
};
#define PROGRAM_NAME __progname
#define LOG_LEVEL_ERROR 0
#define LOG_LEVEL_WARNING 1
#define LOG_LEVEL_STATUS 2
#define LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG 3
/*
* Prefixes for the different logging levels
*/
#define LOG_PREFIX_ERROR "ERROR"
#define LOG_PREFIX_WARNING "WARNING"
#define LOG_PREFIX_STATUS "STATUS"
#define LOG_PREFIX_DEBUG "DEBUG"
/*
*/
static struct logger_t log_global_set;
static const char* LOG_LEVELS[] = { LOG_PREFIX_ERROR,
LOG_PREFIX_WARNING,
LOG_PREFIX_STATUS,
LOG_PREFIX_DEBUG };
void print_to_syslog(const int level, const char* message);
void print_to_file(const int level, const char* message);
/*
* Close remaining file descriptor and reset global params
*/
void cleanup_internal()
{
if (log_global_set.out_file) {
if (!log_global_set.use_stdout) {
fclose(log_global_set.out_file);
}
log_global_set.use_stdout = 0;
log_global_set.out_file = NULL;
}
}
/*
* Reset internal state and set syslog as default target
*/
void logger_reset_state(void)
{
log_global_set.max_log_level = LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS;
cleanup_internal();
log_global_set.logger_func = print_to_syslog;
}
/*
* Print to syslog
*/
void print_to_syslog(const int level, const char* message)
{
syslog(LOG_INFO, "[%s] %s\n", LOG_LEVELS[level], message);
}
/*
* Print to file which can be a regular text file or STDOUT "file"
*/
void print_to_file(const int level, const char* message)
{
struct tm* current_tm;
time_t time_now;
time(&time_now);
current_tm = localtime(&time_now);
int res = fprintf(log_global_set.out_file,
"%s: %02i:%02i:%02i [%s] %s\n"
, PROGRAM_NAME
, current_tm->tm_hour
, current_tm->tm_min
, current_tm->tm_sec
, LOG_LEVELS[level]
, message );
if (res == -1) {
print_to_syslog(LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, "Unable to write to log file!");
return;
}
fflush(log_global_set.out_file);
}
/*
*/
void logger_set_log_level(const int level)
{
log_global_set.max_log_level = level;
}
/*
*/
int logger_set_log_file(const char* filename)
{
cleanup_internal();
log_global_set.out_file = fopen(filename, "a");
if (log_global_set.out_file == NULL) {
log_error("Failed to open file %s error %s", filename, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
log_global_set.logger_func = print_to_file;
return 0;
}
/*
*/
void logger_set_out_stdout()
{
cleanup_internal();
log_global_set.use_stdout = 1;
log_global_set.logger_func = print_to_file;
log_global_set.out_file = stdout;
}
/*
* Logging functions
*/
void log_generic(const int level, const char* format, va_list args)
{
char buffer[256];
vsprintf(buffer, format, args);
log_global_set.logger_func(level, buffer);
}
void log_error(char *format, ...)
{
va_list args;
va_start(args, format);
log_generic(LOG_LEVEL_ERROR, format, args);
va_end(args);
}
void log_warning(char *format, ...)
{
if (log_global_set.max_log_level < LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS) {
return;
}
va_list args;
va_start(args, format);
log_generic(LOG_LEVEL_WARNING, format, args);
va_end(args);
}
void log_status(char *format, ...)
{
if (log_global_set.max_log_level < LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS) {
return;
}
va_list args;
va_start(args, format);
log_generic(LOG_LEVEL_STATUS, format, args);
va_end(args);
}
void log_debug(char *format, ...)
{
if (log_global_set.max_log_level < LOG_MAX_LEVEL_ERROR_WARNING_STATUS_DEBUG) {
return;
}
va_list args;
va_start(args, format);
log_generic(LOG_LEVEL_DEBUG, format, args);
va_end(args);
}
And simple usage example
#include "logger.h"
int main()
{
logger_reset_state();
log_warning("This message goes to syslog");
logger_set_out_stdout();
log_status("Hello!");
logger_set_log_file("log.txt");
log_error("Logger in a file mode!");
return 0;
}
Compile and run:
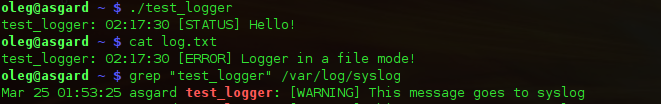
$ gcc main.c logger.c -o test_logger $ ./test_logger
You should see a greeting message on a console. Also, you can find log.txt file with appropriate content and grep program message from the syslog.
 Thanks for reading!
Thanks for reading!
I hope this logger will be useful in your cool projects 🙂
how to view the debug log message
You shoud impove warnings: in debug, warning e.t.c. set const char*